1. What is FNP ? Explain all its phases and give an example for the quadriceps and another for hamstrings
FNP is an advanced
form of flexibility training that involves a stretch and a contraction of the
muscle group. It consist on four phases:
·
Passive stretching: exercise in which a partner helps you to do the stretch, this phase
should be 20 seconds long
·
Isometric contraction : You have to contract the muscle for 6 to 8 seconds and the partner
must block the movement.
·
Rest:
You have to rest for 3 to 5 seconds
·
Passive stretching: You have to repeat the first exercise for 20 seconds and you will see
how your range of movement has increase.
Some
muscles to train FNP are hamstrings and quadriceps:
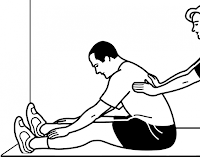
Hamstrings:
Ø Seat down at the floor with your
feet touching a wall
Ø With legs in a straight position try
to touch your feet with both arms
Ø A partner will push your back during
20 seconds, then you will have to contract isometrically during another 8
seconds.
Ø
Relax
Quadriceps :
Ø
Standing
up lift the knee and push the leg at the hip.
Ø
Hold
that position during 20 seconds, then contract isometrically during another 8
seconds.
Ø
Relax
Ø
Execute
the for another 20 seconds
Ø
Repeat
with opposite leg.2. Explain the General Syndrome of adaptation and all its phases. Give an example
General
Syndrome of adaptation is the three-stage process that describes the
physiological changes the body goes through when under stress. Hans Selye, a doctor made the theory of general
syndrome of adaptation, during an experiment with lab rats. He concluded that
the general syndrome of adaptation had three stages: Alarm reaction stage ,resistance
stage and exhaustion stage.
Alarm reaction stage: Refers to the initial symptoms the
body experiences under stress. This natural reaction prepares you to protect
yourself in dangerous situations. Your heart rate increases, you produce
cortisol, and you receive adrenaline, which increases energy. This response occurs in the alarm reaction stage.
Resistance stage: After the alarm reaction stage, the body
begins to normalize. It reduces the cortisol, and your heart rate decreases.
Although your body is recovering, it remains on alert. Some stressful
situations continue for extended periods of time. If you don’t resolve the
stress and your body remains on alert, it adapts and learns how to live with stress.
If you continue in this stage your body continues to secrete the stress hormone,
heart rate remains elevated and you think you manage stress well. If this stage
continuous you can fall on the exhaustion stage
Exhaustion stage: This stage is the result of prolonged stress.
Being with stress for long periods can drain your physical, emotional, and
mental force.
General Syndrome
of adaptation can occur with any type of stress. Stressful events can include a
job loss, medical or financial problems or traumas
Threshold Law
by Arnold Schult is based on the existence of a limit that it is necessary to
cross in order to produce some modification, improvement or adaptation in the
organism without producing unnecessary effort or tiredness
This limit
depends on the physical condition of each one.
This law
must be continuous for adaptation and improvement in the body.
Red and purple
colour are too far of the Threshold, that means, that there isn´t any training
and there are not any improvements
Blue colour
is near to the Threshold that means that there is some training and some
improvements
Yellow
colour exceeds the Threshold, that means that
we don´t get any improvements but we are tired
we don´t get any improvements but we are tired
Training load
refers to the work or stimulus that produces a training session and generates an
adaptation process.
a training
session can be of high load, medium load
and low load. To know that there are 5 compenentes :Intensity, volume, density,
duration and frecuence
Intensity: It refers to the level of effort, it also marks the demand of work. Intensity is divided in percentages :
30-50%= Weak
50-70% = Light
70-80%= Medium
80-90%= Strong
90-100%= Maximus
(Example : 22 minutes running at a medium intensity)
(Example : 22 minutes running at a medium intensity)
Volume : Amount of work done. More volume
means less intensity ( Example: jump 10 times )
Density: Relationship between activity and rest.
Example : Practising speed till I have 120-140 bpm and then rest till I recover)
Duration : Time of application of a stimulus .If
the duration isn´t enough you will not be able to cross the threshold. (Example : Practising speed during
15 seconds)
Frecuence: Number of stimuls applied. (Example:
2 times per week practising speed )
The
principles of training are defined as general rules applicable in the training
of any sport discipline.
They are
aspects that occur by applying physical stress to the body. This may be aimed
at improving performance in some sport.
Some
authors who have written about these principles are Oliver and Zintl.
Classification
of principles of training according to Oliver
- Principles related to the stimulation of physical conditioning.:
- Principles related to the systems to which said stimulus is directed.
- Principles related to the response to stimulus.
Classification
of principles of training according to Zintl
Those who
initiate the adaptation :
- Principles of effective charge stimulation
- Principles of progression: The organism tends to adapt to the stimuli that it is receiving, so it is It is necessary to increase the difficulty or intensity of the stimuli in order to improve the level of development
- Principles of variaty: The organism comes a time when it accommodates the physical work that we are performing and there is a reduction in the trainability that produce this type of exercises. Because of that, this principle say us that we must change our exercises
- Principles of optimal relationship between load and recovery
- Principles of repetition and continuity: When the effort is repeated without the athlete having rested from the previous one, the functional level goes down. The resistance phase of the general adaptation syndrome has not could be fulfilled
- Principles of periodization: Refers to a continuos exercise routine changing a little bit the exercises done before
Those who
exercise specific control of adaptation:
- Principles of individualization and adaptation to age: Each person is completely different so the training session must be adapted to each one
- Principles of progressive specialization
- Principles of alternating
Blibiography:
https://stretchcoach.com/articles/pnf-stretching/
https://www.healthline.com/health/general-adaptation-syndrome#stressful-situations
https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Principio_de_sobrecarga
https://es.scribd.com/doc/78044897/Ley-Del-Umbral-o-Ley-de-Arnold-shultz
https://entrenamientodeportivo.wordpress.com/2018/01/25/los-componentes-de-la-carga/
https://educacionfisicavblog.wordpress.com/2017/09/11/componentes-de-la-carga-de-entrenamiento-volumen-intensidad-densidad-frecuencia-y-duracion/
https://g-se.com/principios-de-entrenamiento_433-bp-E57cfb26e81a24